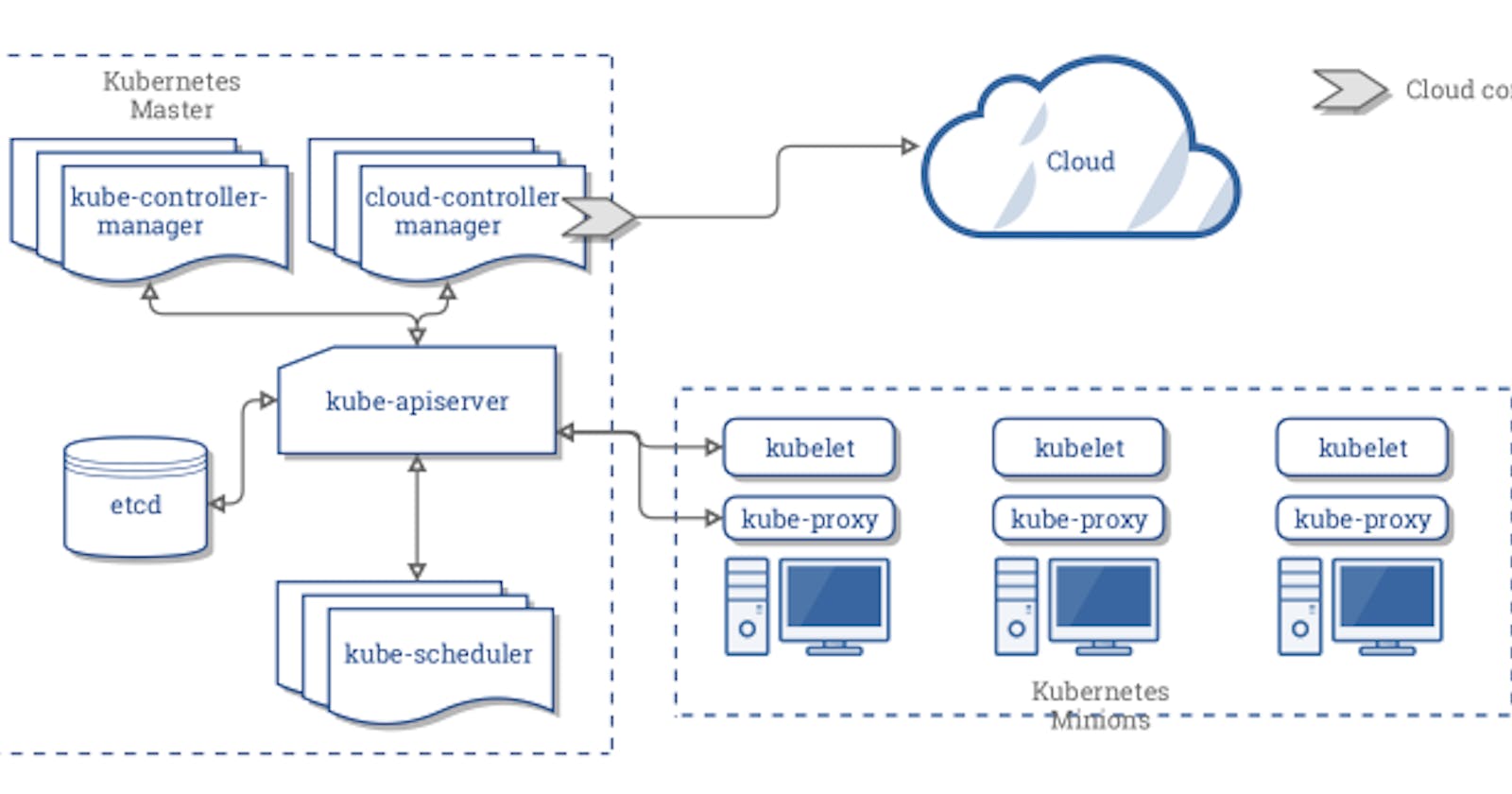
What is Kubernetes
Kubernetes (commonly stylized as k8s) is an open-source container-orchestration system, aiming to provide a simple yet efficient platform for automating deployment, scaling, and operations of application containers across clusters of hosts.
Kubernetes has a series of components architecturally, enabling a mechanism that can provide deployment, maintenance, and extension of applications.
The components are designed to be loosely coupled and scalable so that they can meet various kinds of workloads.
The scalability of the system is largely provided by the Kubernetes API which is used mainly as a scalable internal component and as a container running on Kubernetes.
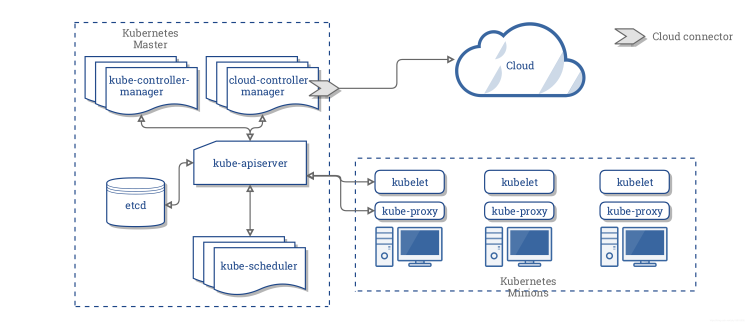
Kubernetes consists mainly of the following core components:
etcdis used as Kubernetes' backing store for all cluster dataapiserverprovides a unique entry for resource operations and provides mechanisms for authentication, authorization, access control, API registration, and discoverycontroller manageris responsible for maintaining the state of the cluster, such as fault detection, automatic expansion, rolling updates, etc.scheduleris responsible for scheduling resources, and scheduling Pods to corresponding machines according to a predetermined scheduling policykubeletis responsible for maintaining the life cycle of the container, and is also responsible for the management of Volume and NetworkContainer runtimeis responsible for image management and the runtime of the Pod and container (CRI)kube-proxyis responsible for providing service discovery and load balancing within the cluster for the kubernetes-service
In addition to the core components, there are some recommended Add-ons:
kube-dnsis responsible for providing DNS services for the entire clusterIngress Controllerprovides external network access for servicesHeapsterprovides resource monitoringDashboardprovides GUIFederationprovides clusters management across Availability ZonesFluentd-elasticsearchprovides cluster log collection, storage and query
Kubernetes and Databases
Database containerization is a hot topic recently, and what benefits can Kubernetes bring to databases?
- Fault recovery: Kubernetes restarts database applications when that fail, or migrates database to other health nodes in the cluster
- Storage management: Kubernetes provides various solutions on storage management so that databases can adopt different storage systems transparently
- Load balancing: Kubernetes Service provides load-balance by distributing external network traffic evenly to different database replications
- Horizontal scalability: Kubernetes can scale the replicas based on the resource utilization of the current database cluster, thereby improving resource utilization rate
Currently many databases such as MySQL, MongoDB and TiDB all work fine on Kubernetes.
Nebula Graph on Kubernetes
Nebula Graph is a distributed, open source graph database that is comprised of graphd (the query engine), storaged (data storage) and metad (meta data). Kubernetes brings the following benefits to Nebula Graph:
- Kubernetes adjust the workload between the different replicas of the graphd, metad and storaged. The three can discover each other by the dns service provided by Kubernetes.
- Kubernetes encapsulate the details of the underlying storage by storageclass, pvc and pv, no matter what kind of storage-system such as cloud-disk or local-disk.
- Kubernetes can deploy Nebula Graph cluster within seconds and upgrade cluster automatically without perception.
- Kubernetes supports self-healing. Kubernetes can restart the crashed single replica without operations engineer.
- Kubernetes scales the cluster horizontally based on the cluster utility to improve the nebula performance.
We will show you the details on deploying Nebula Graph with Kubernetes in the following part.
Deploy
Software And Hardware Requirements
The following list is software and hardware requirements involved in the deployment in this post:
- The operation system is CentOS-7.6.1810 x86_64.
- Virtual machine configuration: 4 CPU + 8G memory + 50G system disk + 50G data disk A + 50G data disk B
- Kubernetes cluster is version v1.16.
- Use local PV as data storage.
Cluster Topology
Following is the cluster topology:

Components to Be Deployed
- Install Helm
- Prepare local disks and install local volume plugin
- Install Nebula Graph cluster
- Install ingress-controller
Install Helm
Helm is the Kubernetes package manager similar to yum on CentOS, or apt-get on Ubuntu. Helm makes deploying clusters more easily with Kubernetes. Since this article does not give a detailed introduction to Helm, read the Helm Getting Started Guide to understand more about Helm.
Download and Install Helm
Installing Helm with the following command in your terminal:
[root@nebula ~]# wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.0.1-linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@nebula ~]# tar -zxvf helm/helm-v3.0.1-linux-amd64.tgz
[root@nebula ~]# mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/bin/helm
[root@nebula ~]# chmod +x /usr/bin/helm</span>
View the Helm Version
You can view Helm version with the command helm version and the output is like the following:
version.BuildInfo{ Version:"v3.0.1", GitCommit:"7c22ef9ce89e0ebeb7125ba2ebf7d421f3e82ffa", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.13.4" }</span>
Prepare Local Disks
Configure each node as follows:
Create Mount Directory
[root@nebula ~] # sudo mkdir -p /mnt/disks</span>
Format Data Disks
[root@nebula ~]# sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/diskA
[root@nebula ~]# sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/diskB</span>
Mount Data Disks
[root@nebula ~]# DISKA_UUID=$(blkid -s UUID -o value /dev/diskA)
[root@nebula ~]# DISKB_UUID=$(blkid -s UUID -o value /dev/diskB)
[root@nebula ~]# sudo mkdir /mnt/disks/$DISKA_UUID
[root@nebula ~]# sudo mkdir /mnt/disks/$DISKB_UUID
[root@nebula ~]# sudo mount -t ext4 /dev/diskA /mnt/disks/$DISKA_UUID
[root@nebula ~]# sudo mount -t ext4 /dev/diskB /mnt/disks/$DISKB_UUID
[root@nebula ~]# echo UUID=`sudo blkid -s UUID -o value /dev/diskA` /mnt/disks/$DISKA_UUID ext4 defaults 0 2 | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
[root@nebula ~]# echo UUID=`sudo blkid -s UUID -o value /dev/diskB` /mnt/disks/$DISKB_UUID ext4 defaults 0 2 | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab</span>
Deploy Local Volume Plugin
[root@nebula ~]# curl https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/sig-storage-local-static-provisioner/archive/v2.3.3.zip
[root@nebula ~]# unzip v2.3.3.zip</span>
Modify the v2.3.3/helm/provisioner/values.yaml file.
#
# Common options.
#
common:
#
# Defines whether to generate service account and role bindings.
#
rbac: true
#
# Defines the namespace where provisioner runs
#
namespace: default
#
# Defines whether to create provisioner namespace
#
createNamespace: false
#
# Beta PV.NodeAffinity field is used by default. If running against pre-1.10
# k8s version, the `useAlphaAPI` flag must be enabled in the configMap.
#
useAlphaAPI: false
#
# Indicates if PVs should be dependents of the owner Node.
#
setPVOwnerRef: false
#
# Provisioner clean volumes in process by default. If set to true, provisioner
# will use Jobs to clean.
#
useJobForCleaning: false
#
# Provisioner name contains Node.UID by default. If set to true, the provisioner
# name will only use Node.Name.
#
useNodeNameOnly: false
#
# Resync period in reflectors will be random between minResyncPeriod and
# 2*minResyncPeriod. Default: 5m0s.
#
#minResyncPeriod: 5m0s
#
# Defines the name of configmap used by Provisioner
#
configMapName: "local-provisioner-config"
#
# Enables or disables Pod Security Policy creation and binding
#
podSecurityPolicy: false
#
# Configure storage classes.
#
classes:
- name: fast-disks # Defines name of storage classes.
# Path on the host where local volumes of this storage class are mounted
# under.
hostDir: /mnt/fast-disks
# Optionally specify mount path of local volumes. By default, we use same
# path as hostDir in container.
# mountDir: /mnt/fast-disks
# The volume mode of created PersistentVolume object. Default to Filesystem
# if not specified.
volumeMode: Filesystem
# Filesystem type to mount.
# It applies only when the source path is a block device,
# and desire volume mode is Filesystem.
# Must be a filesystem type supported by the host operating system.
fsType: ext4
blockCleanerCommand:
# Do a quick reset of the block device during its cleanup.
# - "/scripts/quick_reset.sh"
# or use dd to zero out block dev in two iterations by uncommenting these lines
# - "/scripts/dd_zero.sh"
# - "2"
# or run shred utility for 2 iteration.s
- "/scripts/shred.sh"
- "2"
# or blkdiscard utility by uncommenting the line below.
# - "/scripts/blkdiscard.sh"
# Uncomment to create storage class object with default configuration.
# storageClass: true
# Uncomment to create storage class object and configure it.
# storageClass:
# reclaimPolicy: Delete # Available reclaim policies: Delete/Retain, defaults: Delete.
# isDefaultClass: true # set as default class
#
# Configure DaemonSet for provisioner.
#
daemonset:
#
# Defines the name of a Provisioner
#
name: "local-volume-provisioner"
#
# Defines Provisioner's image name including container registry.
#
image: quay.io/external_storage/local-volume-provisioner:v2.3.3
#
# Defines Image download policy, see kubernetes documentation for available values.
#
#imagePullPolicy: Always
#
# Defines a name of the service account which Provisioner will use to communicate with API server.
#
serviceAccount: local-storage-admin
#
# Defines a name of the Pod Priority Class to use with the Provisioner DaemonSet
#
# Note that if you want to make it critical, specify "system-cluster-critical"
# or "system-node-critical" and deploy in kube-system namespace.
# Ref: https://k8s.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/guaranteed-scheduling-critical-addon-pods/#marking-pod-as-critical
#
#priorityClassName: system-node-critical
# If configured, nodeSelector will add a nodeSelector field to the DaemonSet PodSpec.
#
# NodeSelector constraint for local-volume-provisioner scheduling to nodes.
# Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
nodeSelector: {}
#
# If configured KubeConfigEnv will (optionally) specify the location of kubeconfig file on the node.
# kubeConfigEnv: KUBECONFIG
#
# List of node labels to be copied to the PVs created by the provisioner in a format:
#
# nodeLabels:
# - failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone
# - failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region
#
# If configured, tolerations will add a toleration field to the DaemonSet PodSpec.
#
# Node tolerations for local-volume-provisioner scheduling to nodes with taints.
# Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/
tolerations: []
#
# If configured, resources will set the requests/limits field to the Daemonset PodSpec.
# Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-compute-resources-container/
resources: {}
#
# Configure Prometheus monitoring
#
prometheus:
operator:
## Are you using Prometheus Operator?
enabled: false
serviceMonitor:
## Interval at which Prometheus scrapes the provisioner
interval: 10s
# Namespace Prometheus is installed in
namespace: monitoring
## Defaults to what is used if you follow CoreOS [Prometheus Install Instructions](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/tree/master/helm#tldr)
## [Prometheus Selector Label](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/blob/master/helm/prometheus/templates/prometheus.yaml#L65)
## [Kube Prometheus Selector Label](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/blob/master/helm/kube-prometheus/values.yaml#L298)
selector:
prometheus: kube-prometheus</span>
Modify hostDir: /mnt/fast-disks and # storageClass: true to hostDir: /mnt/disks and storageClass: true respectively, then run:
# Installing [root@nebula ~] # helm install local-static-provisioner v2.3.3/helm/provisioner # List local-static-provisioner deployment [root@nebula ~] # helm list</span>
Deploy Nebula Graph Cluster
Download nebula helm-chart Package
# Downloading nebula [root@nebula ~] # wget https://github.com/vesoft-inc/nebula/archive/master.zip # Unzip [root@nebula ~] # unzip master.zip</span>
Label Kubernetes Slave Nodes
The following is a list of Kubernetes nodes. We need to set the scheduling labels of the worker nodes. We can label 192.168.0.2, 192.168.0.3, 192.168.0.4 with label nebula: "yes".

<noscript><img class="s t u ix ai" src="miro.medium.com/max/3380/1*NeWaf188rP3DW-Wv.." width="1690" height="370" srcSet="miro.medium.com/max/1104/1*NeWaf188rP3DW-Wv.. 552w, miro.medium.com/max/1400/1*NeWaf188rP3DW-Wv.. 700w" sizes="700px" role="presentation"/></noscript>
Kubernetes Nodes
Detailed operations are as follows:
[root@nebula ~] # kubectl label node 192.168.0.2 nebula="yes" --overwrite [root@nebula ~] # kubectl label node 192.168.0.3 nebula="yes" --overwrite [root@nebula ~] # kubectl label node 192.168\. ### Deploying Ingress-controller on one Node</span>
Modify the Default Values for nebula helm chart
Following is the directory list of nebula helm-chart:
master/kubernetes/
└── helm
├── Chart.yaml
├── templates
│ ├── configmap.yaml
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── _helpers.tpl
│ ├── ingress-configmap.yaml\
│ ├── NOTES.txt
│ ├── pdb.yaml
│ ├── service.yaml
│ └── statefulset.yaml
└── values.yaml
2 directories, 10 files</span>
We need to adjust the value of MetadHosts in the yaml file master/kubernetes/values.yaml, and replace the IP list with the IPs of the 3 k8s workers in our environment.
MetadHosts: - 192.168.0.2:44500 - 192.168.0.3:44500 - 192.168.0.4:44500</span>
Install Nebula via Helm
# Installing
[root@nebula ~]# helm install nebula master/kubernetes/helm
# Checking
[root@nebula ~]# helm status nebula
# Checking nebula deployment on the k8s cluster
[root@nebula ~]# kubectl get pod | grep nebula
nebula-graphd-579d89c958-g2j2c 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-graphd-579d89c958-p7829 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-graphd-579d89c958-q74zx 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-metad-0 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-metad-1 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-metad-2 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-storaged-0 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-storaged-1 1/1 Running 0 1m
nebula-storaged-2 1/1 Running 0 1m</span>
Deploy Ingress-controller
Ingress-controller is one of the Add-Ons of Kubernetes. Kubernetes exposes services deployed internally to external users through ingress-controller. Ingress-controller also provides load balancing function, which can distribute external access to different replicas of applications in k8s.

<noscript><img class="s t u ix ai" src="miro.medium.com/max/1492/1*ZQrbNjb4O4jBWkk2.." width="746" height="290" srcSet="miro.medium.com/max/1104/1*ZQrbNjb4O4jBWkk2.. 552w, miro.medium.com/max/1400/1*ZQrbNjb4O4jBWkk2.. 700w" sizes="700px" role="presentation"/></noscript>
Ingress Controller
Select a Node to Deploy Ingress-controller
[root@nebula ~]# kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
192.168.0.1 Ready master 82d v1.16.1
192.168.0.2 Ready <none> 82d v1.16.1
192.168.0.3 Ready <none> 82d v1.16.1
192.168.0.4 Ready <none> 82d v1.16.1
[root@nebula ~]# kubectl label node 192.168.0.4 ingress=yes</span>
Edit the ingress-nginx.yaml deployment file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-configuration
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: tcp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: udp-services
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- nodes
- pods
- secrets
verbs:
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- "extensions"
- "networking.k8s.io"
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- "extensions"
- "networking.k8s.io"
resources:
- ingresses/status
verbs:
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-role
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- pods
- secrets
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
# Defaults to "<election-id>-<ingress-class>"
# Here: "<ingress-controller-leader>-<nginx>"
# This has to be adapted if you change either parameter
# when launching the nginx-ingress-controller.
- "ingress-controller-leader-nginx"
verbs:
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- endpoints
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-role-nisa-binding
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: nginx-ingress-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole-nisa-binding
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: nginx-ingress-clusterrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
namespace: ingress-nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "10254"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
spec:
hostNetwork: true
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app.kubernetes.io/name
operator: In
values:
- ingress-nginx
topologyKey: "ingress-nginx.kubernetes.io/master"
nodeSelector:
ingress: "yes"
serviceAccountName: nginx-ingress-serviceaccount
containers:
- name: nginx-ingress-controller
image: quay.io/kubernetes-ingress-controller/nginx-ingress-controller-amd64:0.26.1
args:
- /nginx-ingress-controller
- --configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/nginx-configuration
- --tcp-services-configmap=default/graphd-services
- --udp-services-configmap=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/udp-services
- --publish-service=$(POD_NAMESPACE)/ingress-nginx
- --annotations-prefix=nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io
- --http-port=8000
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
add:
- NET_BIND_SERVICE
# www-data -> 33
runAsUser: 33
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
- name: https
containerPort: 443
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 10254
scheme: HTTP
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 10</span>
Deploying ingress-nginx.
# Deployment
[root@nebula ~]# kubectl create -f ingress-nginx.yaml
# View deployment
[root@nebula ~]# kubectl get pod -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-controller-mmms7 1/1 Running 2 1m</span>
Access Nebula Graph Cluster in Kubernetes
View which node ingress-nginx is located in:
[root@nebula ~]# kubectl get node -l ingress=yes -owide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
nebula.node23 Ready <none> 1d v1.16.1 192.168.8.23 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 7.6.1810.el7.x86_64 docker://19.3.3</span>
Access Nebula Graph Cluster:
[root@nebula ~] # docker run --rm -ti --net=host vesoft/nebula-console:nightly --addr=192.168.8.23 --port=3699</span>
FAQ
How to deploy Kubernetes cluster?
Please refer to the Official Doc on deployment of high-availability Kubernetes clusters.
You can also refer to Installing Kubernetes with Minikube on how to deploy local Kubernetes cluster with minikube.
How to modify the Nebula Graph cluster parameters?
When using helm install, you can use --set to override the default variables in values.yaml. Please refer to Helm on details.
How to observe nebula cluster status?
You can use the kubectl get pod | grep nebula command or via the kubernetes dashboard.
How to use other disk types?
Please refer to the Storage Classes doc.
References
Originally published at nebula-graph.io.